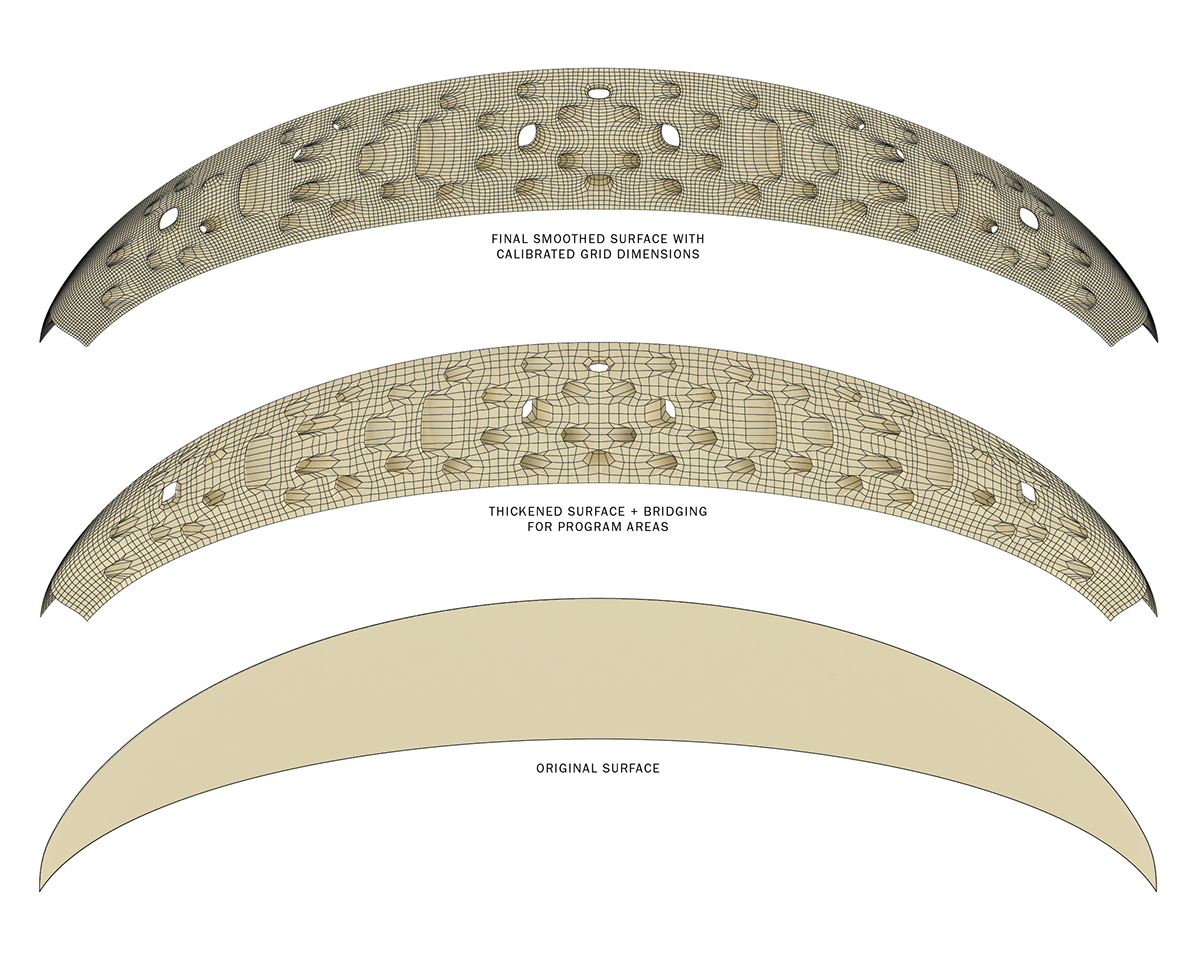
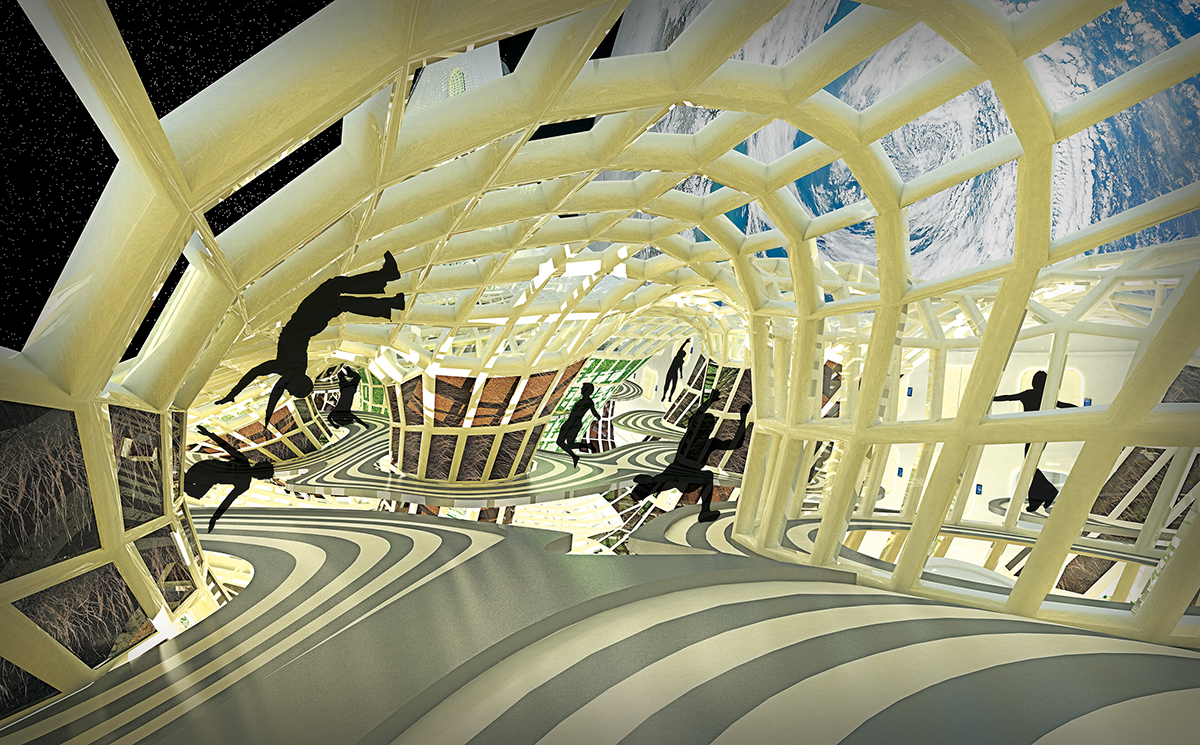
Located 435 miles above the Earth in heliosynchronous orbit, the Solar Arcology exists as part of a global effort to safeguard humanity. The station is enclosed by a gridded structure, one side facing the sun, the other facing Earth. Suspended between these two extremes are the self-sustaining garden facilities that support the colony, dividing the vast space into smaller pockets where the 300 residents conduct research while on stand-by in the event of a global emergency on Earth.
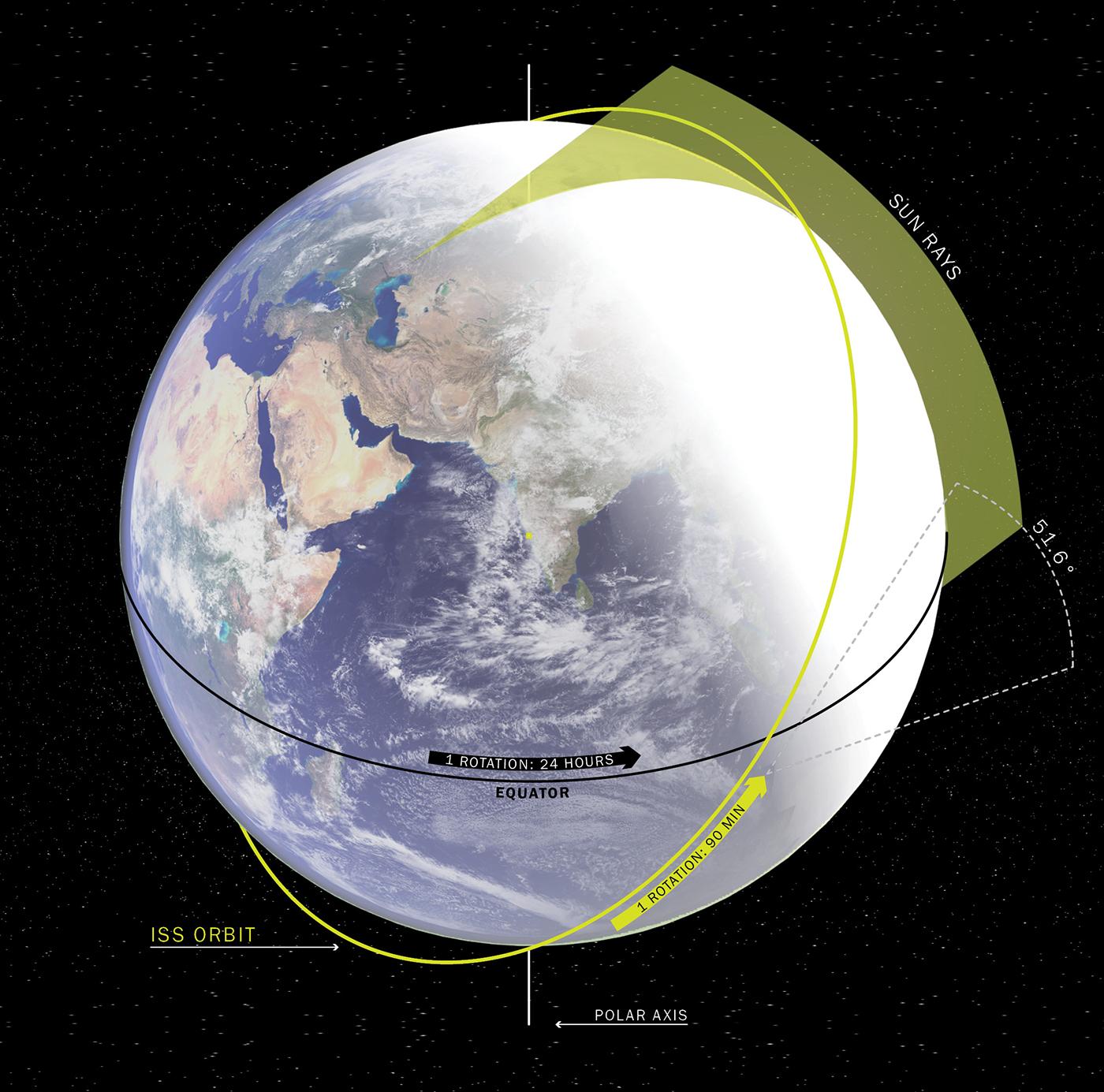
The orbital paths of the ISS and Solar Arcology.
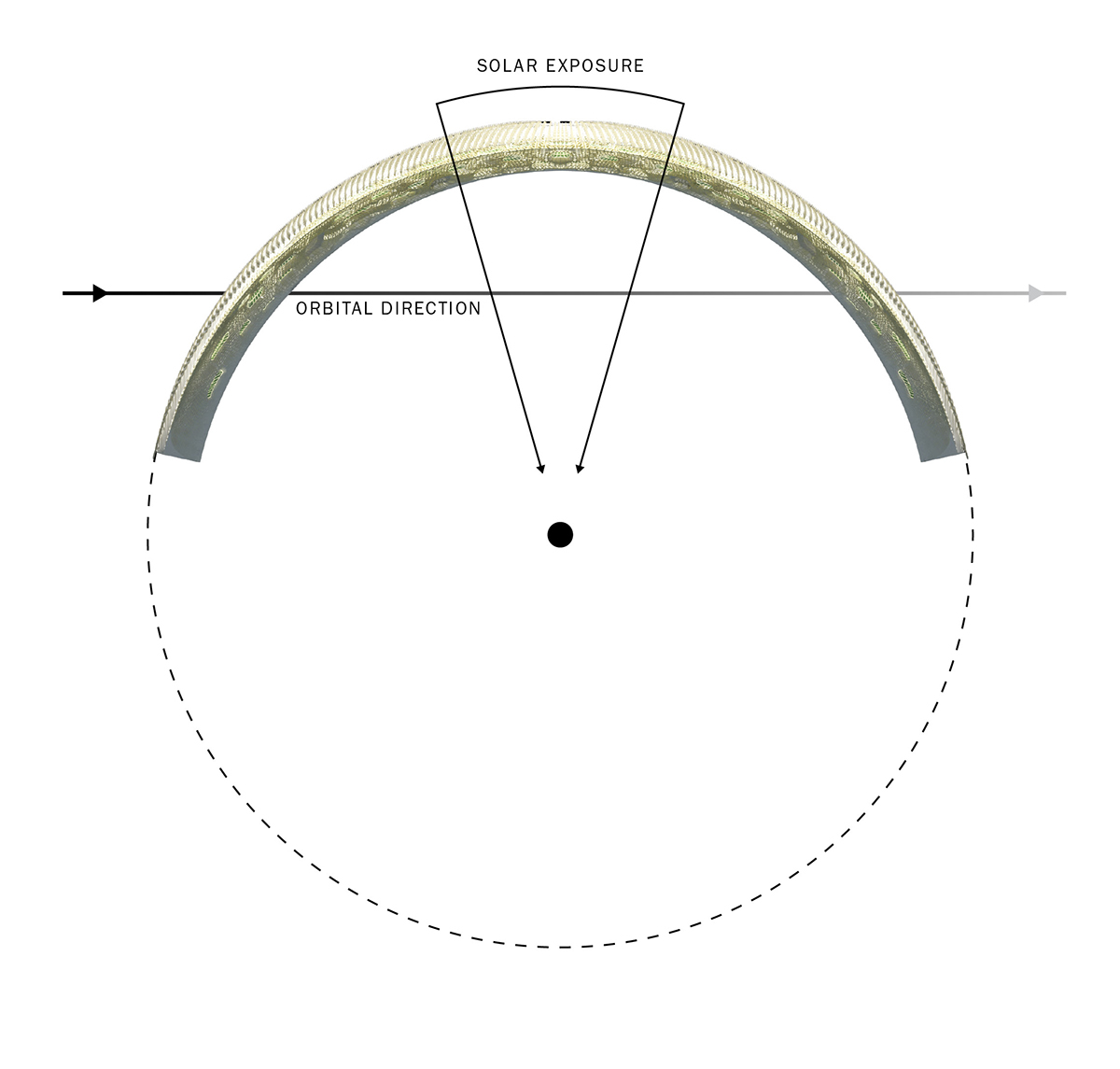
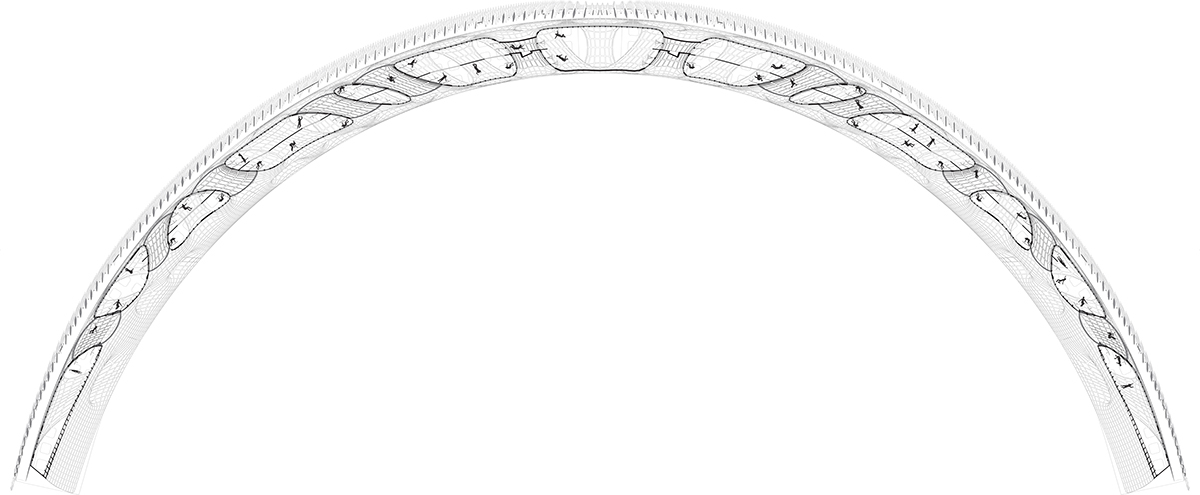
The formal logic of the hemispherical space station, designed as a shield from solar radiation.



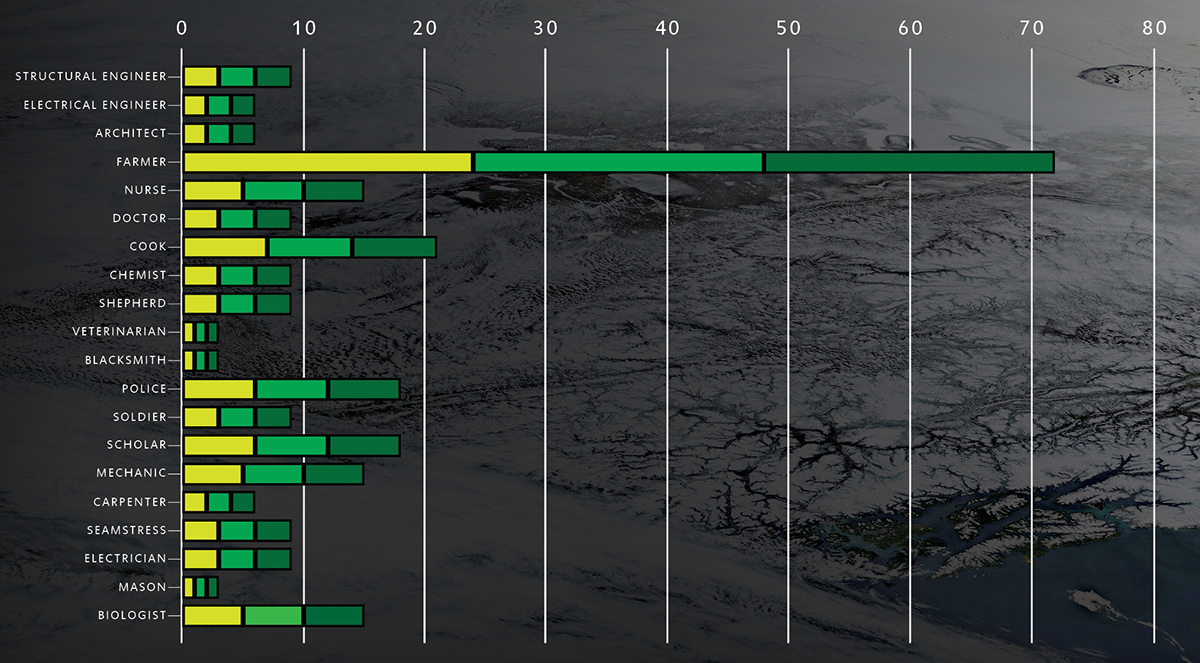
Population breakdown of the space station occupants. A specific number of each knowledge area has been chosen based on their ability to restart civilization after a mass extinction event.

Program distribution.
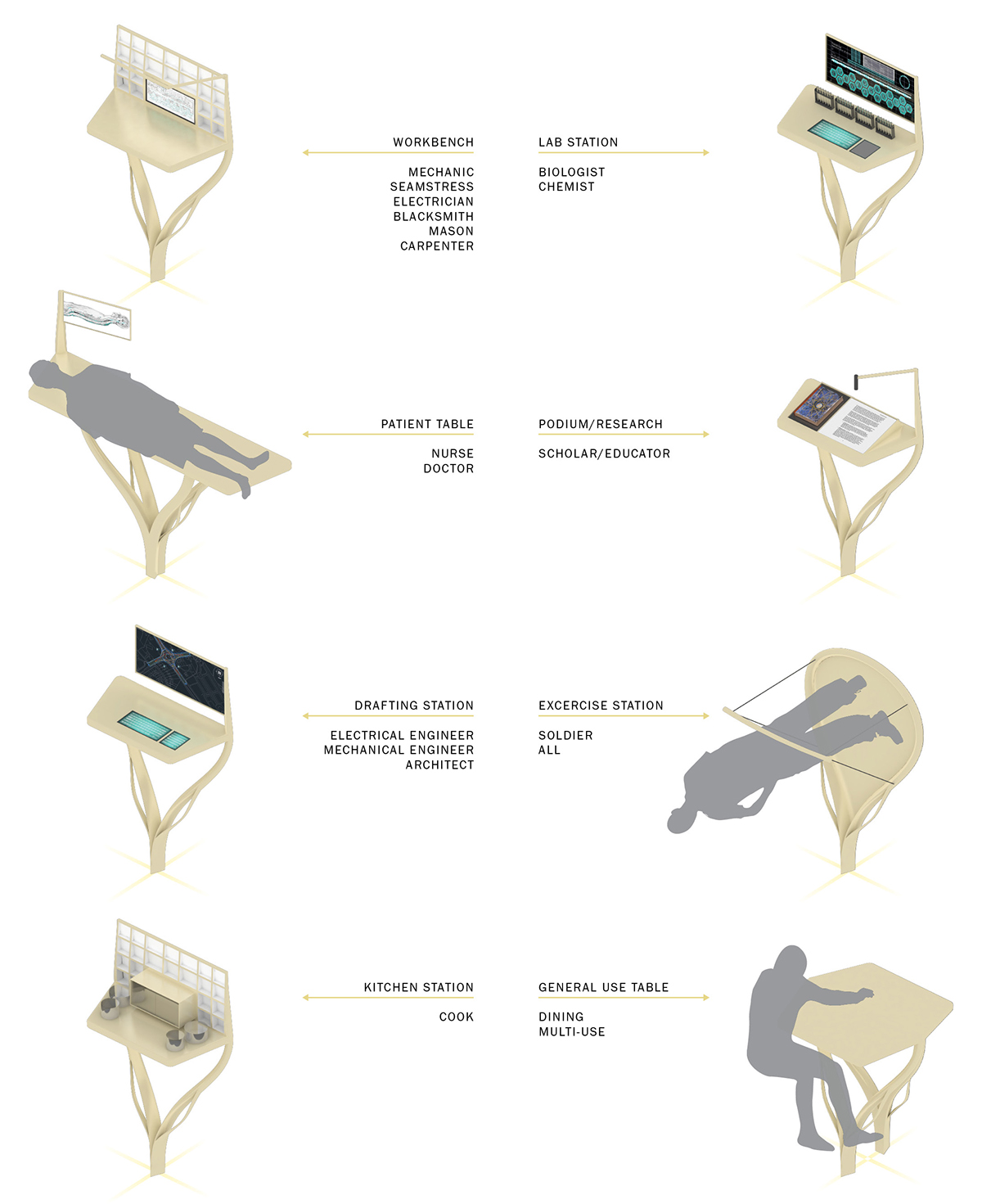
For each vocation represented within the station, there is a custom workstation that can be plugged into the grid structure of the station.
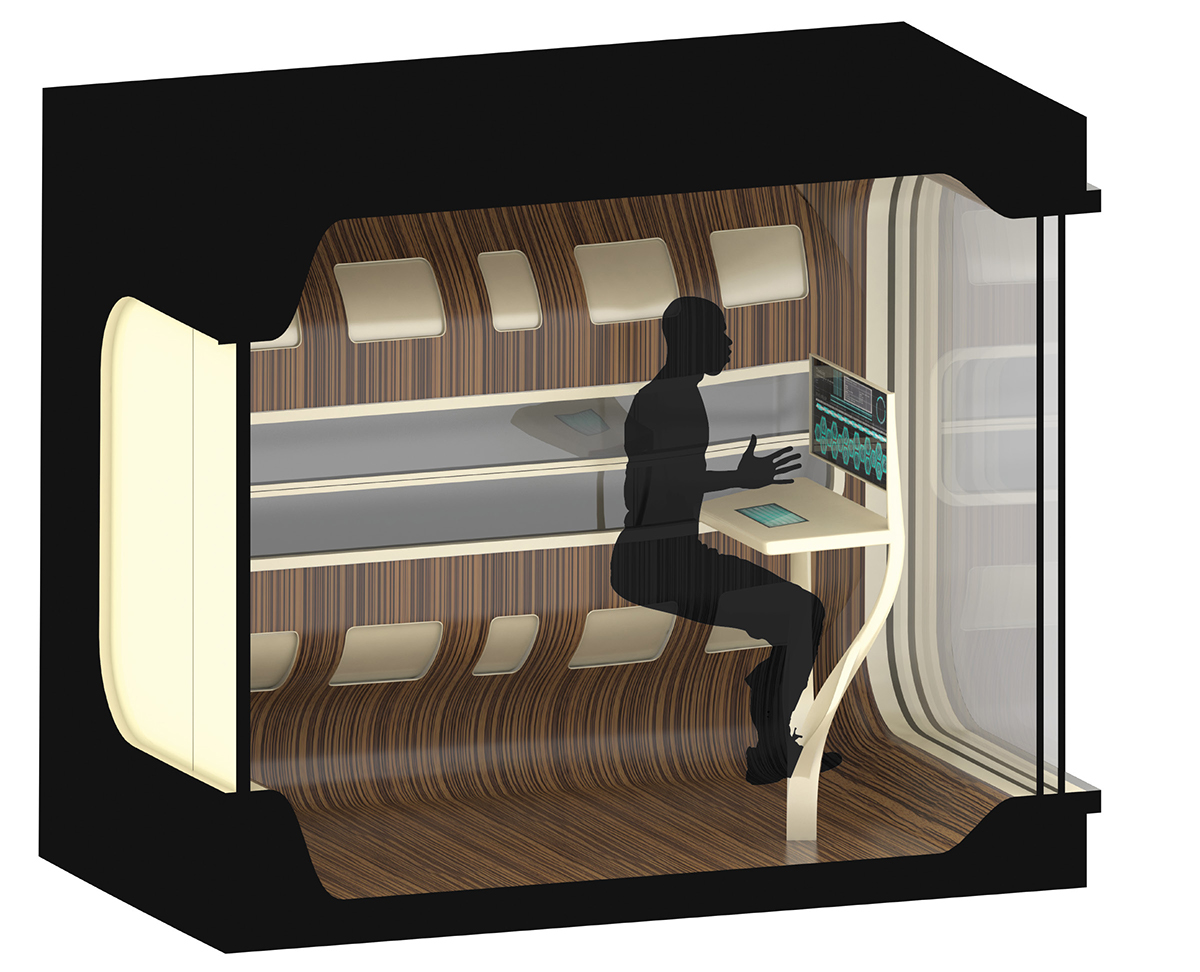
A typical passenger cabin, featuring a large window with a view to earth's surface.
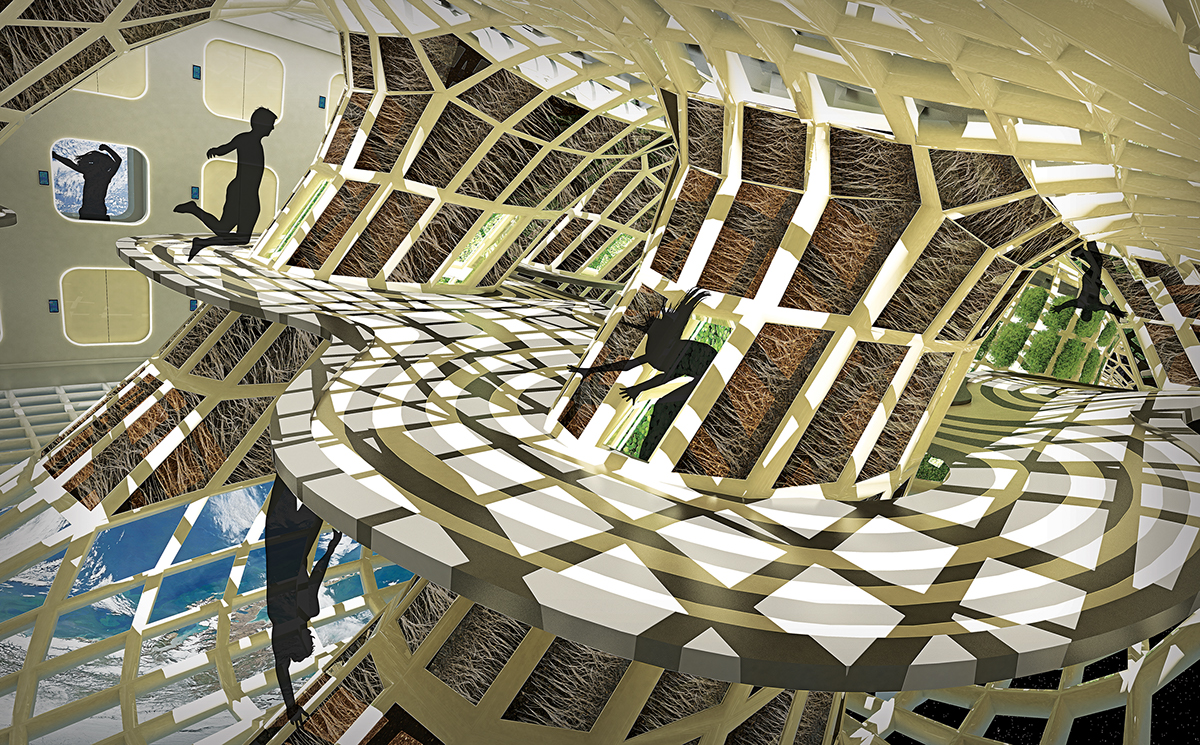

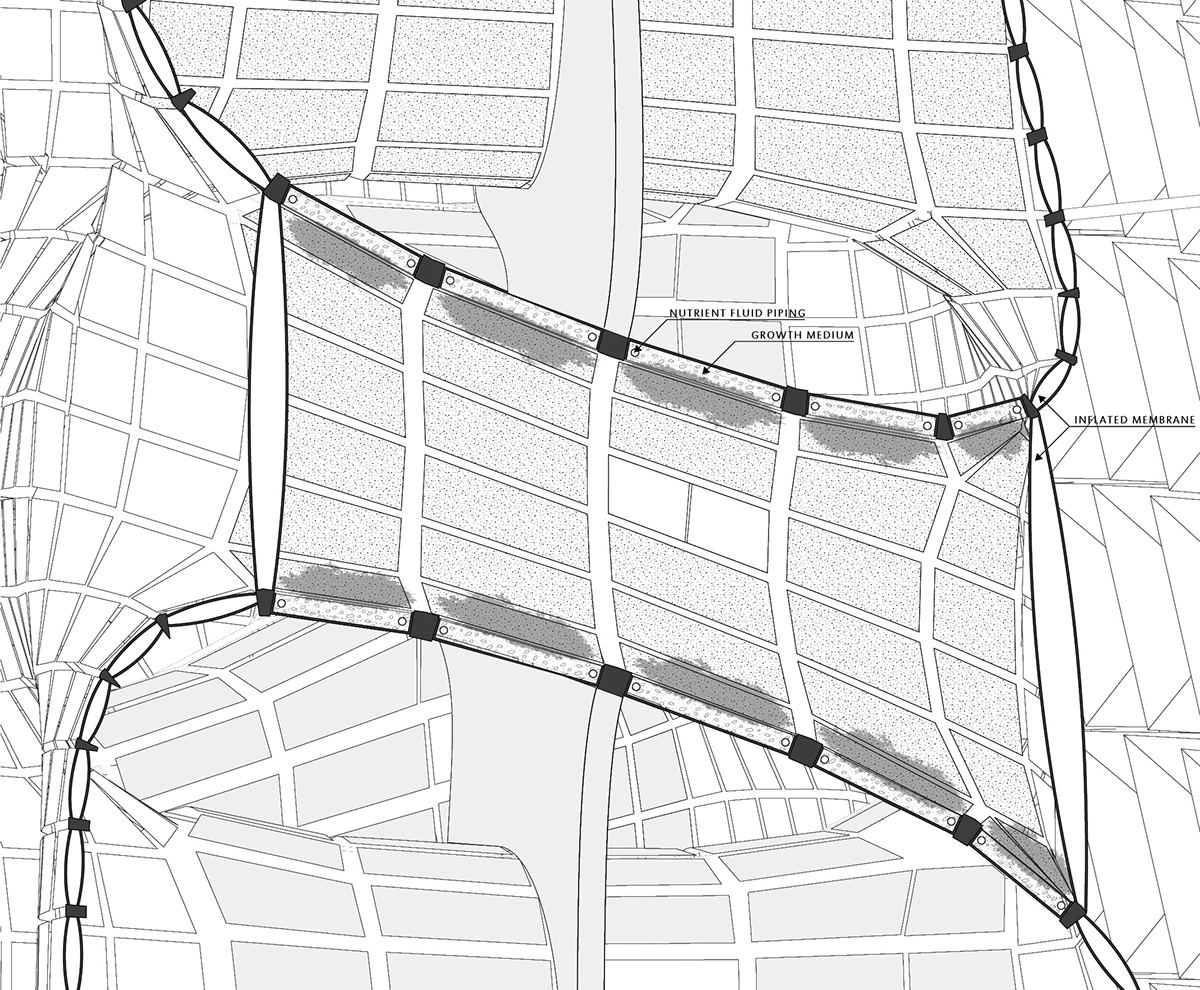
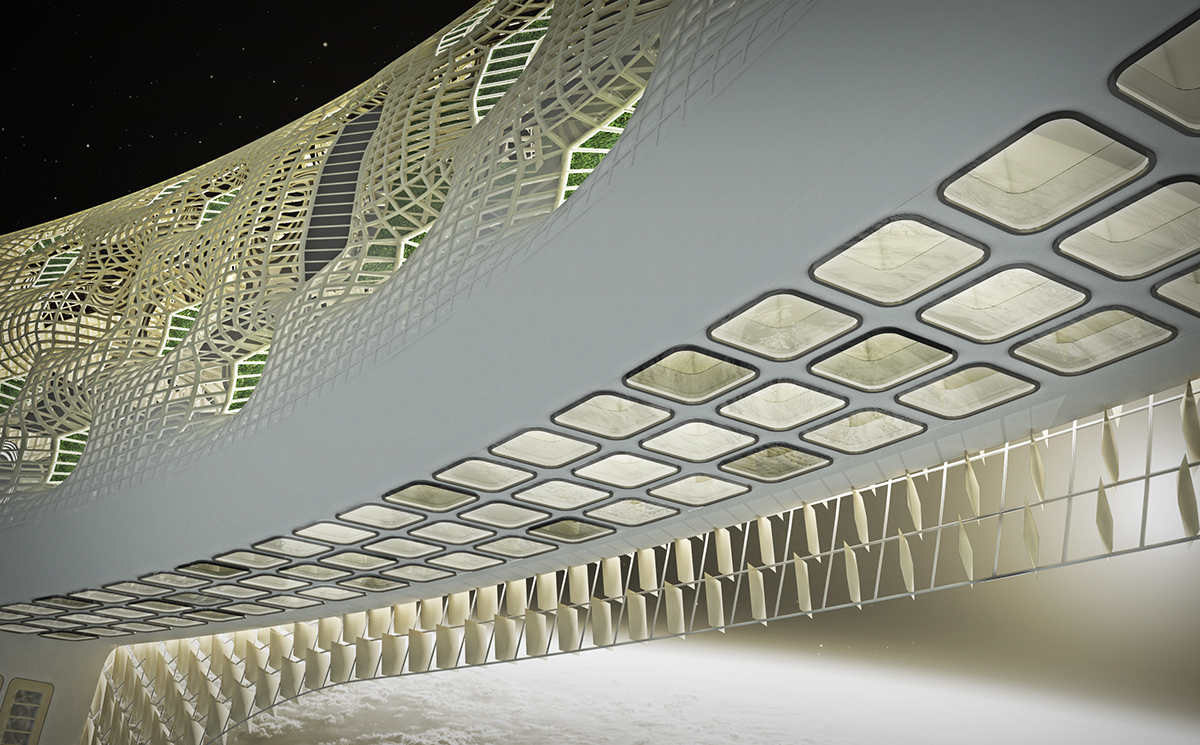

The solar shield of the station can open to allow light to reach the greenhouses and can close to protect the occupants from radiation flares.
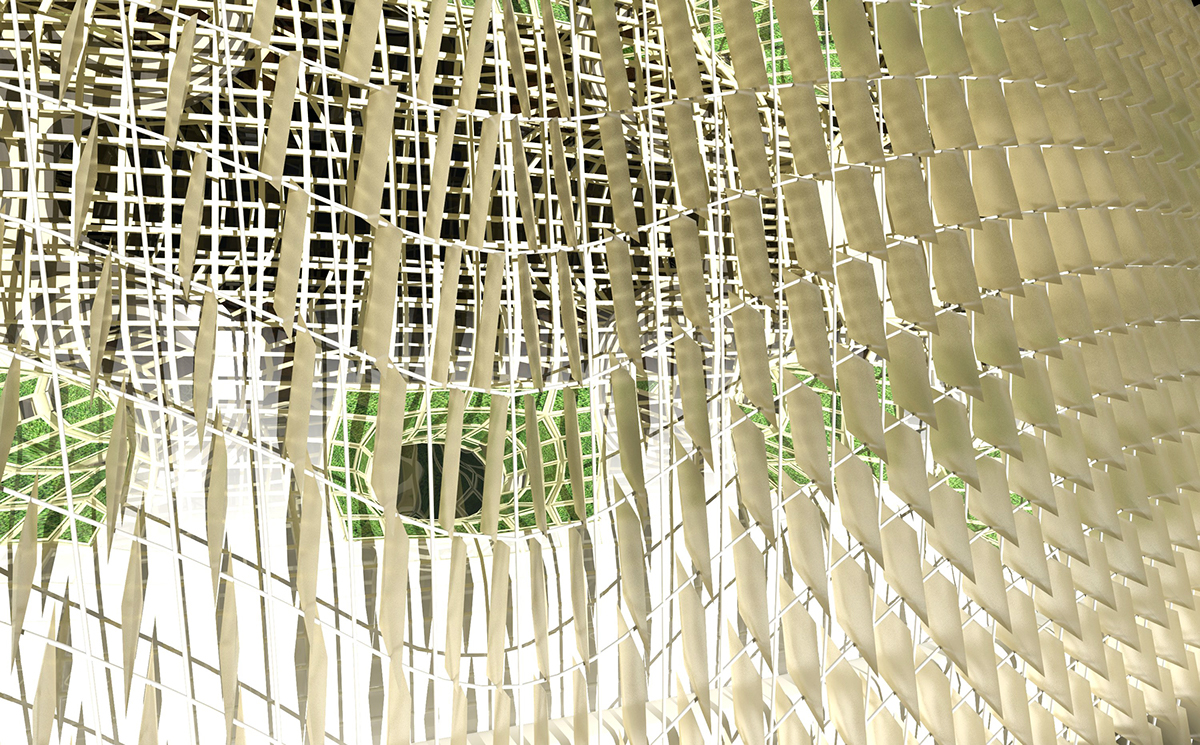

The shield in its open configuration.




